|
 |
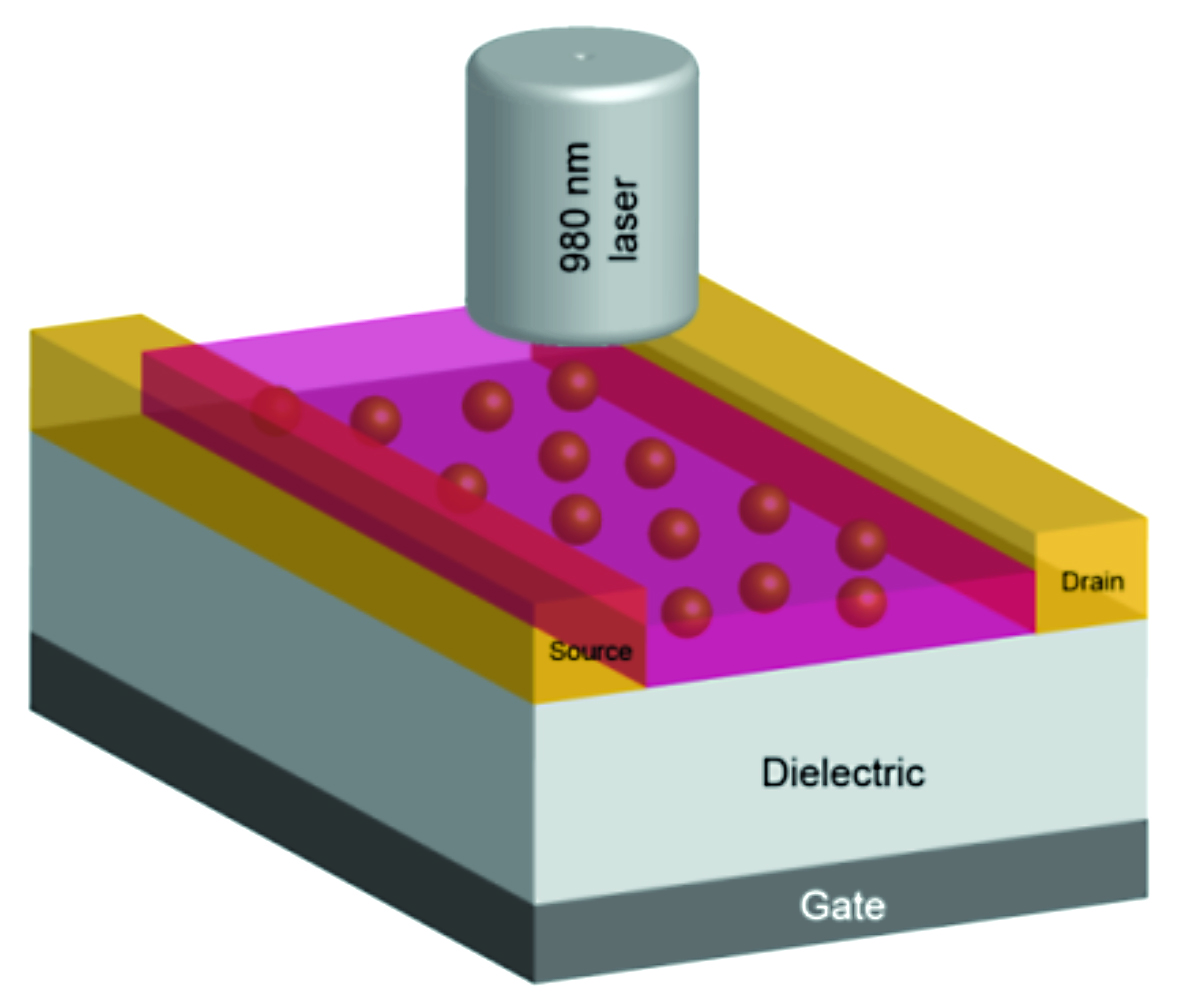
We design a photonic flash memory device where Infrared (IR) light is used for data encryption in addition to an applied voltage bias. In thin film transistor memory architecture, most of the organic or inorganic semiconductors have almost no absorption in IR region due to their typical optical energy bandgap. Up-conversion (UC) describes a nonlinear optical process in which an UC material generates one high-energy photon for every two or more low-energy excitation photons. It has been proved to utilize UC materials for optical manipulation in applications such as solid-state lasers, solar energy conversion, optical storage, cancer therapy, and biological labeling/imaging. Here, we utilize wide bandgap UC materials as nanolamps whose visible emission enhances charge density in the active layer of the memory device. By the absorption of IR light, high-energy photons are emitted by the UC materials. Eventually, the high-energy emission from UC materials are reabsorbed by the active semiconductor layer and more photo-excitons are generated in the active layer which ultimately influence the charge trapping efficiency and data storage levels of the memory device. By increasing the charges in the polymer composite layer, we manipulate the dielectric constant of the medium with light. With a tunable dielectric constant, we aim to obtain a tunable THz photonic device.